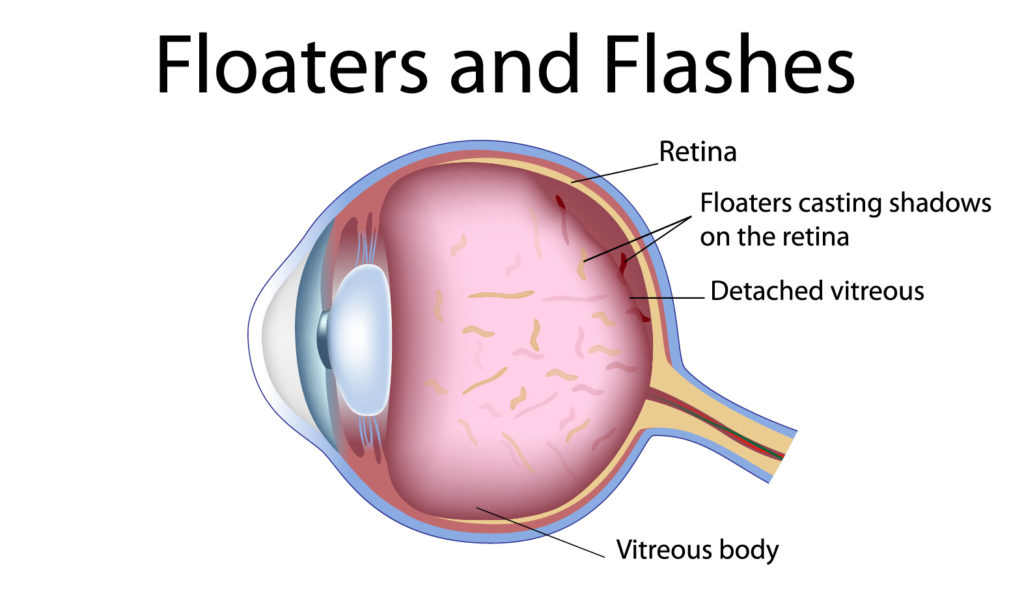
Floaters
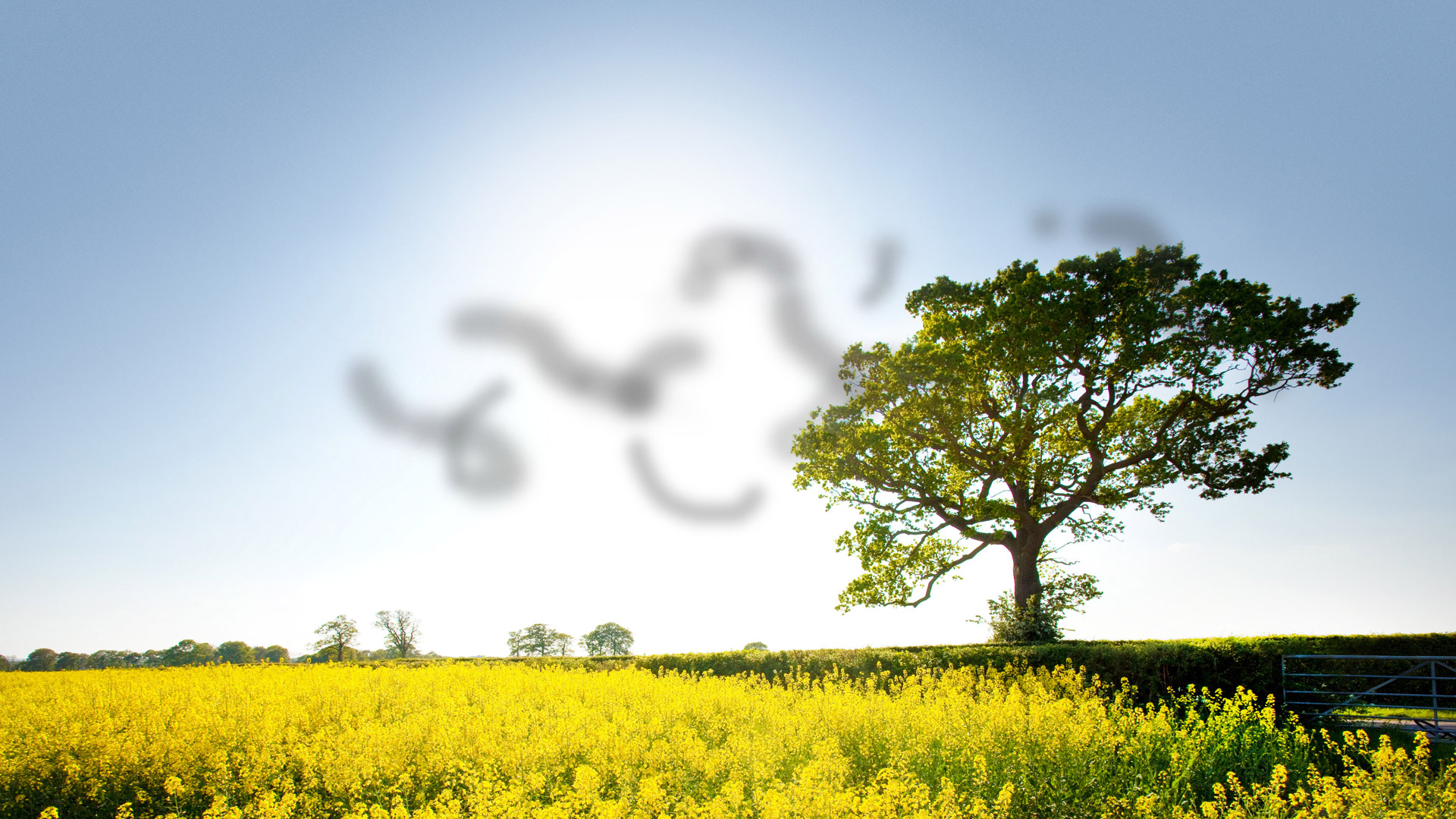
A floater, formally called a posterior vitreous detachment, is often described as a cobweb, a bug or spots moving around a patient’s vision and can be associated with flashes of light. It is due to the gel-like structure within the eye, called the vitreous, becoming more liquid with age, which causes it to suddenly separate from the inside wall of the eye. The concern is that when the vitreous separates it could tear or detach the retina, which could lead to serious vision problems, even blindness. Therefore all patients with floaters or flashes of light should be seen as soon as possible.